The 5G transformation in health care
Did you know that 5G cellular technology has the power to transform health care?
Much of the narrative on the application of 5G technology has focused on its use in mobile devices. This is understandable, given the ubiquity of smartphones in everyday life, and how essential 5G and its predecessor technologies have been in making them more than portable cameras or well-packaged cordless landlines. However, 5G as an enabling technology is widely used in many more applications under the umbrella of the internet of things (IoT). It encompasses everything that is “smart”, from smart energy systems to factories of the future, and it is expected to positively impact different areas of the industry and our daily lives. In health care, the “smart” enabled by 5G technology has the potential to revolutionise the way the service is provided and create a new healthcare ecosystem.
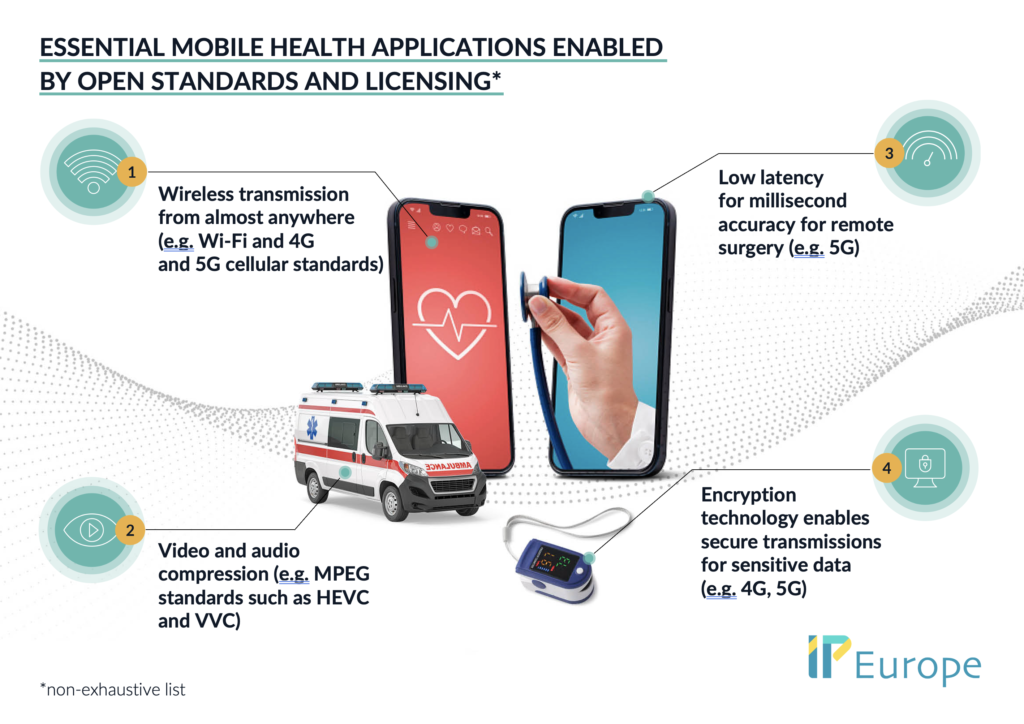
It may be argued that that in combination with other advanced technologies, health care is set to be one of the biggest beneficiaries of the deployment of 5G. With its massive capacity and faster data rates, 5G could prove valuable in telehealth, remote surgery, transferring large medical files, real time monitoring through wearable devices and in the delivering of continual treatment information and support to patients.
A quantum leap forward
Compared with 4G, 5G represents a quantum leap forward with speed up to 100 times faster handling 100 times more connections with ultra-low latency (i.e., lag time between the sending of a piece of information and corresponding response). That promises incredible opportunities for digital health. Whereas 4G and broadband allow for basic one-on-one sessions, 5G offers the possibility to add sensors and virtual reality to teleconferences. That, in turn, enables the constant monitoring of vital signs, even from afar. The full potential for 5G in health care involves integration with AI, the cloud, big data analytics, geo-locations sensors and real time monitors.
This transformation is aligned with the 4Ps of health care: predictive, preventative, personalised and participatory.
Predictivity will be enabled by the constant flow of data on patients’ vital signs. Combined with geolocation data and evolving testing and diagnostic profiles, it will make medicine more preventative and better able to identify those at risk of being infected with or inadvertently transmitting infectious diseases to others. Real time monitoring will make medicine more personalised, and patients will become more active participants in their health by interacting with a 5G enabled ecosystem of devices, such as wearables tracking and sharing live and accurate data. From providing care from the point of first response through post-hospitalisation, to providing services in-home and improving quality service access to remote populations, greater connectivity is already visibly transforming our healthcare systems worldwide.
5G transformation in emergency services
The example of this transformation starts with the automatic request for assistance and transport in case of emergencies (offered, e.g., by wearables as smart watches) – for instance, recognising a medical emergency based on live vitals, and triggering a request to dispatch for an ambulance. Following that, the secure transmission of data captured from various monitoring devices – both personal and on the ambulance – can help assess the patient’s condition to and from the hospital. In parallel to providing remote support from the hospital to first responders on route, potential interventions and special needs can be anticipated and prepared prior to the patient’s arrival, resulting in a smoother and faster response, and ultimately better care.
Perhaps most strikingly, where the specialised personnel needed to treat a patient are not physically available, the improved 5G connectivity can make remote intervention a meaningful possibility through on-site imaging capability or remotely directed robotic assistance.
5G applications in home care
Patients’ subsequent care and monitoring can likewise be facilitated by 5G enabled equipment at home, lowering the burden for healthcare practitioners and hospital infrastructure, as well as providing more autonomy to the patient. While online consultations have become normal practice due to the pandemic, 5G enables a better service and care, offering high-definition virtual consultation and supporting patient compliance with medication.
Complemented by other technological advances and underpinned by a secure network, 5G connectivity enables better healthcare services, including to those located in remote areas. In doing so it offers cost-effective opportunities and can help provide greater efficiency and equitable access to quality of health care both in Europe and abroad.
Like this article and want to learn more? Sign up for our newsletter using the form below!
Further reading
10 5G Healthcare use cases transforming digital health
MDIC Publishes First Landscape Analysis of 5G in Healthcare – MDIC
5G and Healthcare | CONNECT University
How 5G Will Change Healthcare – Insider Intelligence Trends, Forecasts & Statistics
5G Will Transform Healthcare Delivery
How 5G Wireless (and Concomitant Technologies) Will Revolutionize Healthcare?




